top of page



Symptoms of Pierce's disease of grapevine caused by Xylella fastidiosa.
Blackstock Winery, GA, in 2014.
Twitching motility of a colony of Xylella fastidiosa on PWG medium observed under a microscope.



Biofilm formation by Xylella fastidiosa in the channels of a microfluidic chamber with PD3 medium.
Set-up of a microfluidic chamber showing the inlet tubes, tubings connected to inlet and outlet tubes and the chamber.
Disease symptom of leaf scorch of blueberry infected with Xylella fastidiosa strain AlmaEM3 in a green house experiment.
Fusion PCR to construct gene deletion templates in Xylella fastidiosa. Bands in lanes 2-4 are individual PCR fragments for upstream, antibiotic marker, and downstream segments of the targeted genes. Bands in fifth and sixth lane are fusion products of the above three. Band in the seventh lane is a control band without antibiotic insertion. Fragments were fused by overlap-extension PCR. Fused product applied to cells gives rise to mutants with target gene deletions.

Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) images of Xylella fastidiosa cells. thread like structure emerging from the cell poles are pili (longer type IV and shorter type I) Xylella cells lack flagella.


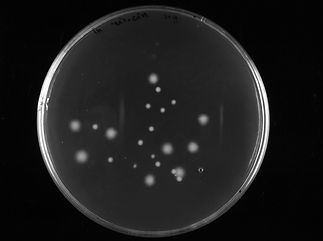
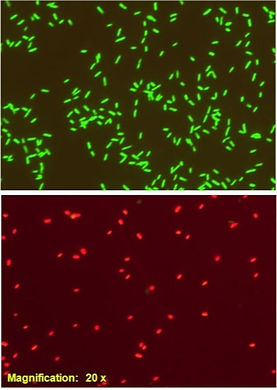
Activity testing of purified tailocin (a type of bacteriocin also referred to as phage-tail like) from a producing strain with its target strain. The clear spots are the result of the target strain lawn killed by tailocin.


There is a region that has recombined. Harvest tool alignment of Xylella genomes to visualize variable recombinogenic regions.
That's the protocol to use to generate gene knock-outs and complemented strains in Xylella and potentially to any other naturally transformable bacteria.
Reference mapping of reads generated by Illumina NextSeq sequencing of a bacteriocin resistant mutant to the parental wild-type genome to identify the causal mutation.
bottom of page




